CASE REPORT
Pilomatrixoma Mimicking a Pyogenic Granuloma Clinically: A Rare Case Report from Syria
Lina Al-Soufi1, Moatasem Hussein Al-janabi2, *, Boshra Wannous3, Rana Issa4, Zuheir Al-shehabi5
Article Information
Identifiers and Pagination:
Year: 2022Volume: 16
E-location ID: e187437222207200
Publisher ID: e187437222207200
DOI: 10.2174/18743722-v16-e2207200
Article History:
Received Date: 26/4/2022Revision Received Date: 20/5/2022
Acceptance Date: 6/6/2022
Electronic publication date: 21/09/2022
Collection year: 2022

open-access license: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC-BY 4.0), a copy of which is available at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode. This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
Background:
Pilomatrixoma is a benign skin tumor arising from the hair matrix cells. It is typically found in the head and neck region. However, few cases of pilomatrixoma that mimic a pyogenic granuloma have been reported. Clinicians should be aware of it because it may recurrence and transform into a malignant tumor.
Case Presentation:
We report a rare case of a 9-year-old boy who presented with an asymptomatic mass on the left cheek for 2 months. Clinically, it was diagnosed as a pyogenic granuloma. An excisional biopsy was performed and sent to the pathology department for histopathological study. Histological examination showed that it was a pilomatrixoma. The patient was discharged on the same day, without any complications.
Conclusion:
Pilomatrixoma is often misdiagnosed clinically; therefore, the definitive diagnosis of skin tumors should be made after a histologic examination of the excisional mass. Surgical resection with wide margins was the optimal treatment for pilomatrixoma because local recurrence may occur.
1. INTRODUCTION
Pilomatrixoma, also referred to as pilomatricoma, or calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe is a rare neoplasm arising from the hair matrix [1]. It is usually a solitary lesion and is most commonly found on the head, neck region, and upper extremities [2, 3]. It presents as a slow-growing, subcutaneous nodule smaller than 3 cm [3]. Pilomatrixomas are often confused clinically with other benign masses [4]. Here, we report a rare case of pilomatrixoma mimicking pyogenic granuloma on the left cheek in a 9-year-old boy.
2. CASE REPORT
A 9-year-old boy first visited the dermatology clinic due to an asymptomatic nodular mass on the left cheek, which had been presented for 2 months (Fig. 1).
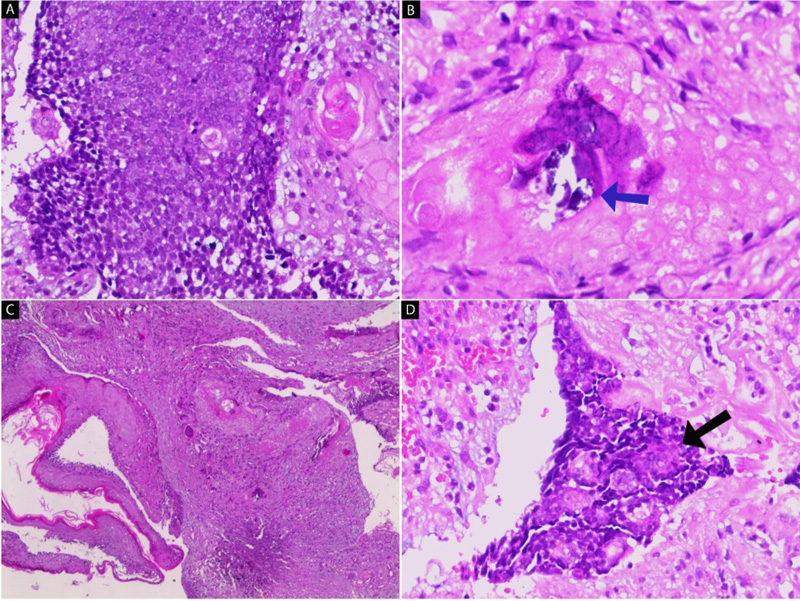
Clinical examination revealed that the mass was red, fixed, well-defined and it was smaller than 1 cm in diameter. Routine blood investigations (CBC) revealed no abnormality. The clinical diagnosis was made as pyogenic granuloma. The patient did not use any specific drugs and had no history of allergy. There was no tumor history in her family; particularly no history of skin tumors. An excisional biopsy was performed and sent to the pathology department for histopathological study. A pathologic review of the excised mass demonstrated a relatively well-circumscribed, whitish solid lesion, measuring 2.5 cm in maximum diameter. The cut surface was gray-white with chalky deposits. Microscopically, the tumor is composed of a lobular proliferation of small basaloid cells (Fig. 2A). Ghost cells, enlarged epithelial cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm, but without a nucleus, are seen (Fig. 2B). The tumor cells are surrounded by fibroblastic stroma (Fig. 2C). with foreign body giant cells (Fig. 2D). The final diagnosis was pilomatrixoma. The patient was discharged on the same day, without any complications.
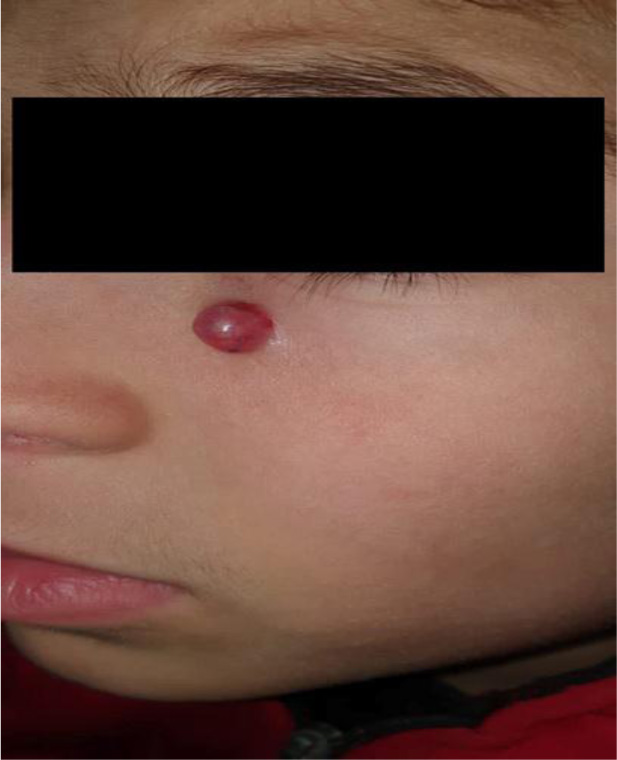 |
Fig. (1). Firm, red, nodular nodule on the left cheek. |
3. DISCUSSION
Pilomatrixoma, first described as a “calcified epithelioma of Malherbe” in 1880, is a nodular, benign tumor arising from the hair matrix. It occurs predominantly in children and young adults, and most of the cases are located on the head, neck, and upper extremities [5-7]. It presents as a slow-growing, firm nodule less than 3 cm [1, 3]. Microscopically, it is composed of solid nests of small basaloid cells and shadow cells (ghost cells) that are eosinophilic-stained with nuclear concentration and disappearance [2]. Local recurrence may occur if excision is incomplete; therefore, wide local excision with confirmed negative margins represents the treatment of choice for pilomatrixoma [1, 2]. Malignant transformation of pilomatrixoma into a pilomatrix carcinoma should be suspected in cases with repeated local recurrences [3, 4]. The differential diagnoses of pilomatrixoma include basal cell carcinoma, pyogenic granuloma, and epidermal cyst [4, 8]. However, pyogenic granuloma of the skin appears as rapidly growing, smooth or lobulated, reddish exophytic vascular nodules, in any size from a few millimeters to several centimeters, and it usually occurs in teenagers, young adults, and during pregnancy [9, 10].
CONCLUSION
Pilomatrixoma is often misdiagnosed clinically; therefore, the definitive diagnosis of skin tumors should be made after a histologic examination of the excisional mass. Surgical resection with wide margins was the optimal treatment for pilomatrixoma because local recurrence may occur.
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
Not applicable.
HUMAN AND ANIMAL RIGHTS
No animals/humans were used for studies that are the basis of this research.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Written consent was obtained.
STANDARDS OF REPORTING
CARE guidelines were followed.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
Not applicable.
FUNDING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.